
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comElectronic products with high performance have become increasingly popular over the years. The printed circuit boards drive most of these products, which have stable temperatures and a high dielectric constant. Using today's best PCB materials, PCB manufacturers meet this requirement. By replacing FR-4 with materials that ensure efficient power distribution, thermal management, and efficient power efficiency, traditional FR-4 will cease to exist. With its many ranges of substrates that guarantee high performance with low signal losses, Rogers Corporation is the world's leading manufacturer of high-performance PCB materials. Founded in 1858, Rogers is a leader in providing metal-organic composite materials for high-frequency and high-speed circuits, microwaves, and RF products.
This article provides you the detail information about Rogers PCB material including its types, materials, and design tips.
Table of Content
Rogers PCB is a type of printed circuit board (PCB) material made from a combination of epoxy and ceramic. It is well known for its high dielectric constant, low loss tangent, and high thermal conductivity, making it an ideal material for high-frequency applications. It is used in a wide range of electronics, such as cellular phones, satellite communications, and wireless networks.
Rogers PCB is produced using the raw materials of the Rogers Company. Rogers company manufactures the laminate materials that are often used for manufacturing circuit boards. The rogers PCB is a type of high-frequency board, quite different from the traditional PCB board materials, epoxy resin. It uses the ceramic base as the material of high frequency. The major advantage of rogers PCB is the temperature stability and superior dielectric constant.
Rogers PCB has a major application in high-speed electronic designs, radio frequency applications, and commercial microwaves. The low water absorption capacity of this rogers PCB is ideal for the application of high humidity. Other Rogers PCB applications include RF identification tags, power amplifiers, automotive radar, sensors, etc.
Some of the features of the rogers PCB include the following:
There are many reasons to choose Rogers PCBs over other options, as Rogers material is preferred due to its ability to deliver the best results in challenging environments, as well as its quality and practicality of use. Even though Rogers PCBs are expensive compared to other materials, they have a lot of advantages and can perform well in poor conditions. In terms of cost, durability, performance, production, and electrical properties, FR-4 material can provide the basic standard for PCB substrates. Rogers materials have some important features over other materials because they have better performance and electrical properties:
Rogers RO300 series are ceramic-filled PTFE composites and high-frequency circuit materials. Thus, they are useful for RF and microwave applications in commercial settings. In addition to the dielectric constant, the RO3000 PCB series have consistent mechanical properties. Thus, the multi-layer board design becomes easier. Besides, the dielectric constant for this Rogers PCB series is steady with the high temperature.
Advantages of the R03000 series
A Rogers RO4000 series prepreg and hydrocarbon ceramic laminate is an industry leader. Consequently, they are suitable for microwaves and millimeter-waves. Also, they use low-loss materials. It also provides circuit fabrication.
Advantages of R04000 Series
It supports the 5G wireless application. Besides, this rogers PCB is suitable for automotive radar applications with a frequency of 77 GHz.
It provides affordable models along with advanced ceramic-filled PTFE materials. Thus, the stability of this Roger PCB delivers a better solution for broadband applications.
It provides stable electrical and mechanical properties. Besides, it provides dielectric constant across various ranges of temperatures.
In addition to having a high dielectric constant (DK) control and low loss capabilities, Rogers 4350B material is ideal for high-power RF applications.
The Rogers 4003 model makes use of 1080 and 1674 glass fabric styles.
Despite significant oxidation resistance and increased temperatures, this 4835 laminate retains a high level of stability.
In terms of performance and processing capabilities, this laminate is perfect. In addition, the low-loss laminate contains ceramic thermostat materials filled with hydrocarbons.
The materials used in Rogers PCB are categorized into three main categories; metal claddings, laminates, and bonding materials.
The characteristics of the metal claddings are:
Rolled
Electrodeposited
Resistive Foil
Electro deposited Reverse Treated
The basic nature of the laminates is as follows:
Hydrocarbon
Woven Glass Reinforced Modified Epoxy Laminates
Woven Glass ReinforcedAntenna Grade Laminates
Filled PTFE Composite
Woven Glass Reinforced Modified Epoxy IMS
The nature of bonding materials includes:
Woven Glass
Prepreg
Ceramic PTFE Bondply
Hydrocarbon and
Thermoset Thermal
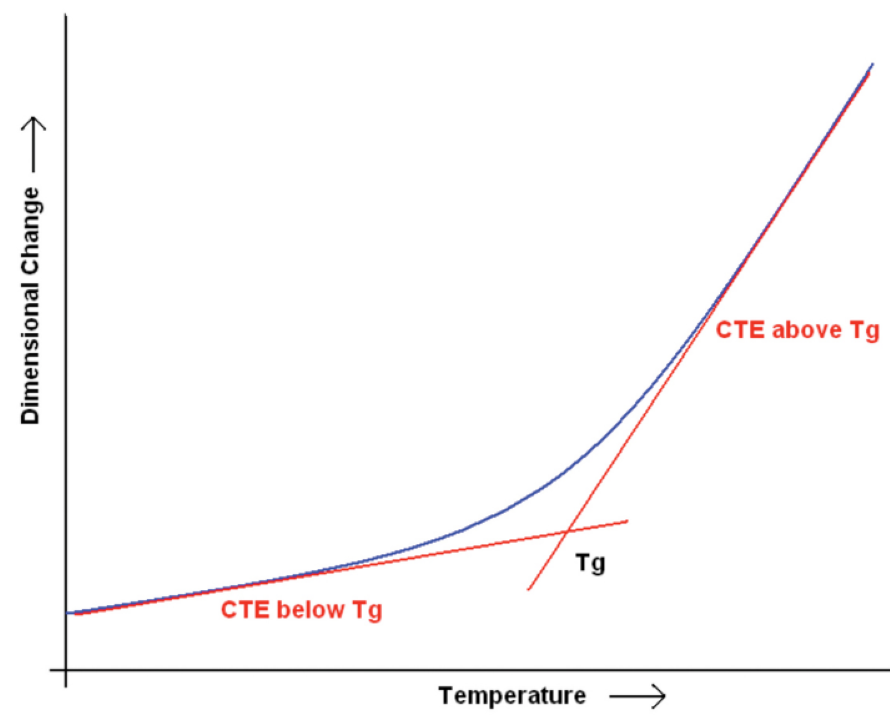
Materials expand as their temperature increases and vice versa. As a result, the PCB material also relaxes or expands due to high or low temperatures. It is usually determined when the expansion will occur by a temperature limit, also called the glass transition temperature (Tg). PCB materials below the glass transition temperature (Tg) do not expand, while if the temperature increases over the threshold level, expansion commences. The higher the glass transition temperature (Tg), the higher the performance and quality. Deformation due to thermal expansion will be less likely to occur when the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is higher. In this way, the coefficient of thermal expansion is related to deformation. If CTE is low, deformation will begin earlier and cannot be used at high temperatures as it will deform, causing malfunctions or affecting the result. Parts per million, also known as (ppm), are the units of deformation.
Rogers materials have a coefficient of thermal expansion of nearly 17ppm/°C. This is similar to copper and is enough to reduce the tendency for misshape. Besides, it also improves dimensional stability.
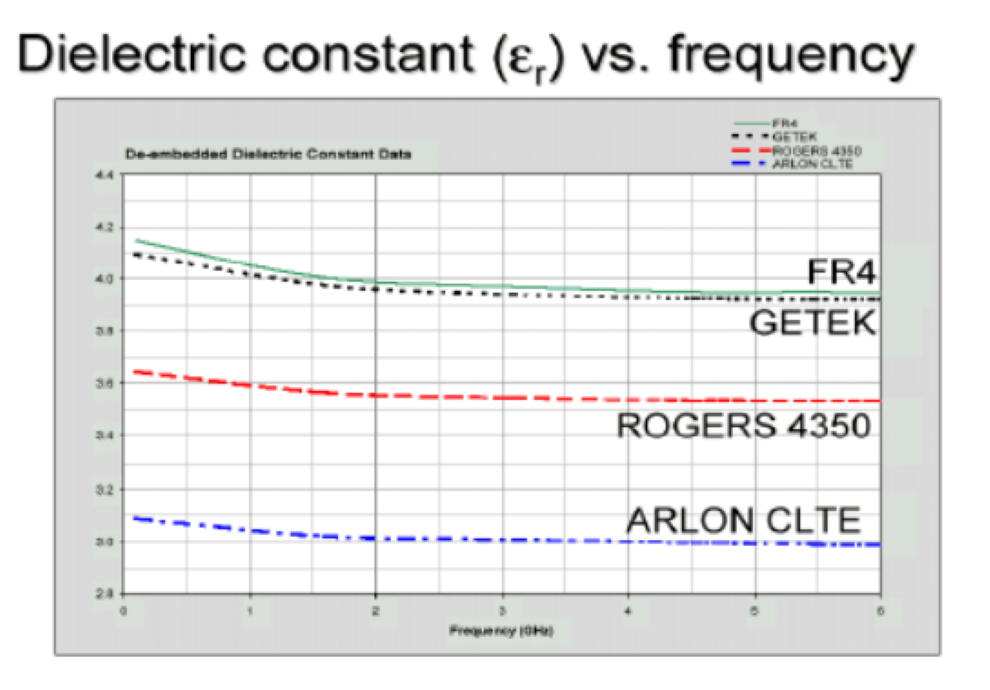
Dielectric Constant is the ability to of storing the charge. The higher dielectric constant value has a high capacitance value, resulting in more charges stored in the materials. This provides a higher voltage across the PCB, reducing the size of the PCB.
The dielectric value is constant for the wide range of frequencies which helps to perform better in the broadband application.
Rogers materials can work in wide frequency ranges with constant dielectric constant making it the best choice for broadband applications. The smaller value of the dielectric constant of Rogers PCB gives the advantage to use them in temperature-sensitive devices because of smaller temperature coefficient values. Besides, the various series of Rogers PCB materials can operate in wide frequency ranges resulting in high-speed performance in both wireless and wired communication systems.
Thus, based on your requirements, you need to check all these factors while designing your PCB.
Most PCB materials do absorb moisture from the environment. There is no idea of devices or materials that don't absorb some percent of moisture from nature. The current PCB materials have a moisture absorption rate of 0.01-0.02%. Thus, it is required to have a lower rate of moisture absorbent since the presence of moisture could affect the thermal and electrical conductivity of the PCB materials. Rogers PCB materials and other materials also absorb moisture from the air. But the better thing with Rogers PCB is that it has comparatively lower absorbent properties than the other PCBs. This results in better thermal and electrical properties. Thus, the Rogers PCB can work in any environment with less chance of failure. Therefore, while designing Rogers PCB, one needs to consider this one of the important factors.
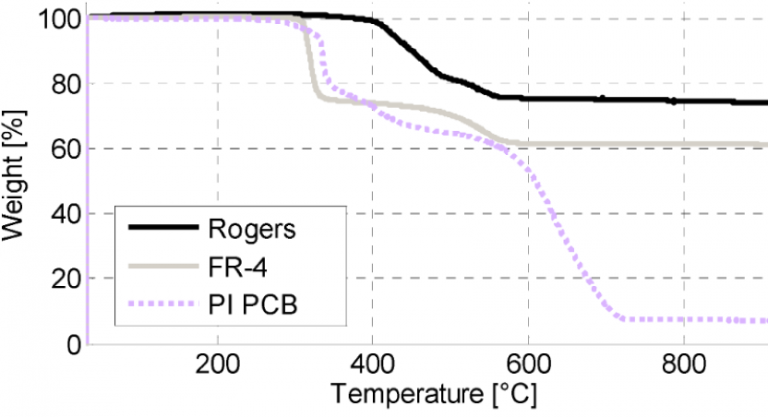
The project has a definite operating temperature-based one in which the PCB board materials are selected. Rogers PCB is fixed in the case of sensitive materials at higher temperatures. The temperature problem is to be considered. If not, it will decay with time. The rogers materials have a higher decomposition temperature than conventional PCB types. Thus, while designing the rogers PCB, the designer should consider the temperature resistivity for various applications.
While designing the PCB, the designer should consider the dissipation factor, including power loss for the components that usually increase with the increased operating frequency. The heat-conductive nature of the materials usually determines the dissipation factor. The improper distribution of heat in the PCB can cause mechanical and electrical failure of the system that could result in serious accidents.
By combining Rogers PCB layers with FR-4 layers, we can achieve reduced cost and maximum performance compared to if we used only Rogers layers. Thus, this process should use Rogers PCB cores instead of prepregs for this process.
FR-4 stack up with 6 layers is shown below. Because prepreg is less expensive than cores, it is placed on the outside to minimize cost. A foil build is often referred to as this.
Rogers layers are required on the outside layers, but the core is usually found on the layers that need them. Below is an example with 6 layers but with 3 cores instead of 2. This configuration is sometimes called a "core build" or "cap construction" board. Rogers PCB is a high-frequency circuit board that has ceramic laminates and reinforced hydrocarbon. A Rogers PCB may be made from cores and prepregs, but most often, the top two copper layers are carried on the core, while the rest of the board is made from standard FR-4 to reduce the cost. The PCB materials absorb the signal, due to which it has less signal loss compared to that of FR-4. At higher frequencies, the signal loss is greater in FR-4 materials. This is also the signal length and design dependent.
PCB with FR-4 materials is preferred due to their low cost, reliability, and well-understood electrical and mechanical properties. They are used in various applications ranging from microwave designs to audio circuits. Unfortunately, FR-4 printed circuit boards are not suitable for high-frequency applications. Rogers created the most well-known high-frequency-special laminates. Its materials have a constant dielectric reduction of close to 20% when compared to FR-4 printed circuit boards.
The best way to determine whether your project will benefit from high-frequency laminates is to assess electrical and mechanical requirements. If you find both variations are too broad, Rogers PCB material is a better option.
The material used is most important when producing printed circuit boards, though it may require a high cost. However, it is not the only issue that knows the content value when it comes to the loss factor or Df. FR-4 printed circuit boards will be affected or reduced. The losses are greater when compared to printed circuit boards made from Rogers materials.
In other words, when compared to Rogers PCB, FR-4 materials have a higher dissipation factor, especially at high frequencies. Typical values for FR-4 printed circuit boards are around 0.020 and close to 0.004 for Rogers boards. Dissipation of FR-4 materials increases with frequency. High-frequency laminates primarily have a frequency-dependent stable dissipation characteristic.
The signal loss is minimized with the lower dissipation factor in FR-4. Also, the automated assembly process and the processing of FR-4 materials make them easier in the assembly and manufacturing process.
Impedance is the measure of the current opposition when applying voltage. In many design applications, the stable impedance is essential and is an area where the materials like Rogers and FR-4 are applied.
FR-4, despite its low cost, is prone to high variations in the dielectric constant with the change in temperature across the length and width of the substrate. In terms of impedance stability, Rogers' material has a wider range of dielectric constants than FR-4 content.
High-frequency laminates are preferable for circuits that require little variation over wide temperature ranges. In this case, you may need to use printed circuit boards made of Rogers materials rather than FR-4 materials, especially if most of your operations involve working in high-temperature environments.
The dielectric constant of any material measures a substance's ability to store some electrical energy across an electrical field. When it comes to dielectric constant, FR-4 has a dielectric constant of about 4.5, which is much lower than Roger's material, which has a dielectric constant of about 6.15 to 11.
The dielectric constant of FR-4 is comparatively higher than that of plastic materials. Using FR-4 materials can save at least 25% of PCB made from such materials. Other factors that make FR-4 articles available include their lightweight, moisture resistance, and high dielectric strength. Even though the Rogers PCB has a higher dielectric than FR-4, you can go with FR-4. FR-4 and Rogers 4350b and 4350 are similar manufacturing processes, although FR-4 stores electrical energy effectively.
Thus, PCB with higher dialect trends breaks easier when subjected to intense electric fields.
Space exploration has recently increased, with many countries attempting to send people into space. When it comes to space applications, the materials used in the production of printed circuit boards are very important.
Some materials may not perform as expected. FR-4 and Rogers are two very different materials regarding their applicability or use in space. Outgassing occurs in space. Outgassing occurs when trapped gases in powder coating are released during the curing process. Corrosive materials or moisture can penetrate the surface through the pinholes and destroy some parts.
Although FR-4 materials provide an excellent balance of electrical stability, durability, cost, and manufacturability, Rogers materials are considered some of the best in space applications. In short, they are low outgassing and suitable for almost any type of space exploration or use.
A wide range of electrical devices requires heat management materials. Because the temperature of these products maintains at specific levels, thermal management materials are required when designing PCBs. The thermal coefficient of the dielectric constant is used to characterize or gauge printed circuit board materials. This is nearly 200 ppm per degree Celsius change for FR-4 materials. Although a small number, it can cause significant temperature variations.
The working condition of little variation over the higher temperature is better for working with Rogers material. Thus, we can say that Rogers material performs better in temperature management. Therefore, Rogers materials, a high 0-frequency thermoset, are more robust and excellent for higher temperatures.
| Factors | FR-4 Material | Rogers Material |
|---|---|---|
| Dissipation factor (DF) | 0.020 | 0.004 |
| Price | Affordable | Expensive |
| Thermal Management | Doesn’t handle high temperatures well. | The Rogers material manages high temperatures perfectly. |
| Performance | Decent | Remarkable |
| Dielectric Constant (DK) | 4.5 | 6.15 to 11 |
| Impedance Stability | Lower polarity and it doesn’t stabilize charges well. | Higher polarity stabilizes charges effectively. |
| Applications | The FR-4 isn’t so ideal for space applications. | Rogers is a better option for space applications. |
Difference between Rogers and Ceramic
Rogers PCB vs RF PCB
Rogers PCB vs Teflon PCB
Rogers PCB is designed to operate in digital products with higher signal integrity and speed. Besides, it also withstands a higher range of temperatures. Thus, while designing your PCB, ensure the application of your product. The selection of the wrong materials can directly impact your project's overall cost and delay your project's overall timing.
At NextPCB, we have our expertise and engineers who work with our clients from the beginning of the project and provide the stacks ups, designs, and materials for the manufacturing and assembling. NextPCB is the leading manufacturer that fulfills all your PCB manufacturing requirements and needs. You can contact us anytime, and feel free to ask any questions and learn about your PCB requirements.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|