
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comIn the field of electronics, we frequently encounter terms like CPU, MCU, MPU, SoC, DSP, ECU, GPU, and FPGA. These are all common types of chips or processors, yet they differ significantly in architecture, functionality, and application scenarios. Some may find it difficult to distinguish between them, so let's delve into their definitions and differences.

Definition: The core component of a computer system, responsible for executing instructions and processing data.
Function: Comprising an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and a control unit (CU), the CPU performs computations and coordinates other hardware components. It executes a series of instructions to accomplish complex calculations, control input and output operations, and serves as the core of general-purpose computing systems such as desktops and laptops.
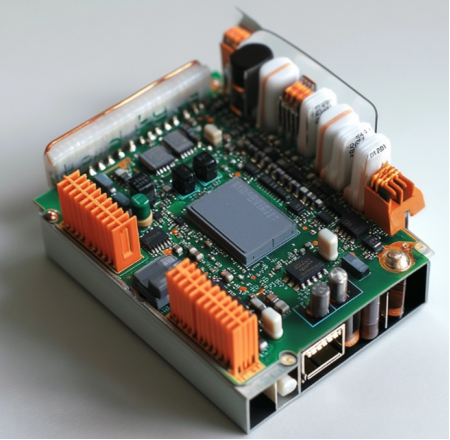
Definition: Also known as a microcontroller or single-chip microcomputer, an MCU integrates a CPU, memory, timers, input/output interfaces, and other functional modules into a single chip.
Function: Primarily used for controlling various electronic devices, including home appliances, automotive electronics, and industrial control systems. MCUs are characterized by low power consumption, low cost, high integration, and ease of development.
Definition: A chip that integrates a CPU, memory, peripheral controllers, and bus interfaces.
Function: Similar to a CPU, an MPU is a standalone processing chip that executes complex general-purpose computing tasks, runs operating systems, and supports various applications in smartphones, personal computers, and servers.
Definition: A highly integrated chip that incorporates a microprocessor, analog and digital IP cores, memory, and necessary interface circuits into a single chip.
Function: Designed to create a complete electronic system, SoCs enhance integration, reduce size, lower power consumption, and improve overall system performance.

Definition: A specialized microprocessor optimized for processing digital signals.
Function: Designed for real-time, high-speed processing of digital signals, DSPs excel in mathematical operations such as multiply-accumulate (MAC). They are widely used in audio processing, image processing, and communication applications.
Definition: A control unit in automotive electronics that consists of microcontrollers or microprocessors and is responsible for managing various electronic systems in vehicles, such as engine control, transmission control, and stability control.
Function: ECUs receive input data from various sensors, process it using internal algorithms, and exchange data with other automotive systems via communication buses to ensure vehicle functionality and safety.
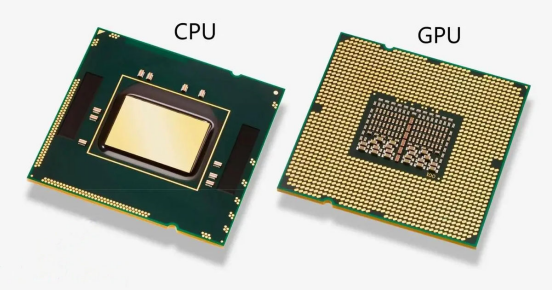
Definition: A specialized microprocessor dedicated to handling graphics computations in personal computers, workstations, gaming consoles, and some mobile devices.
Function: GPUs are optimized for parallel processing and can rapidly process large amounts of graphical data. They play a crucial role in gaming, graphics rendering, and deep learning, accelerating image generation and processing tasks.
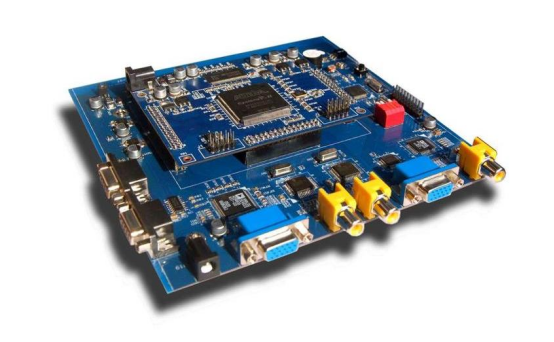
Definition: An advanced programmable logic device that allows users to configure its internal logic functions as needed.
Function: Users can program FPGAs to implement various digital circuits, including specific algorithms, interface conversions, and logic control. They are commonly used for rapid prototyping, hardware acceleration, and specialized applications.
Conclusion
In summary, CPU, MCU, MPU, SoC, DSP, ECU, GPU, and FPGA exhibit significant differences in functionality, architecture, performance, and application scenarios. Each of these processors and chips possesses unique features and advantages, collectively driving advancements in electronic technology.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|