
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com
Capacitors are electrical components that store energy in an electric field. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including filters, amplifiers, and oscillators.
One important factor to consider when using capacitors is their polarity. Polarized capacitors have a positive and negative terminal, and must be connected to a circuit in the correct polarity. If a polarized capacitor is connected in the wrong polarity, it can be damaged or even explode.
Non-polarized capacitors do not have a positive or negative terminal and can be connected to a circuit in any polarity.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to capacitor polarity. We will cover the following topics:
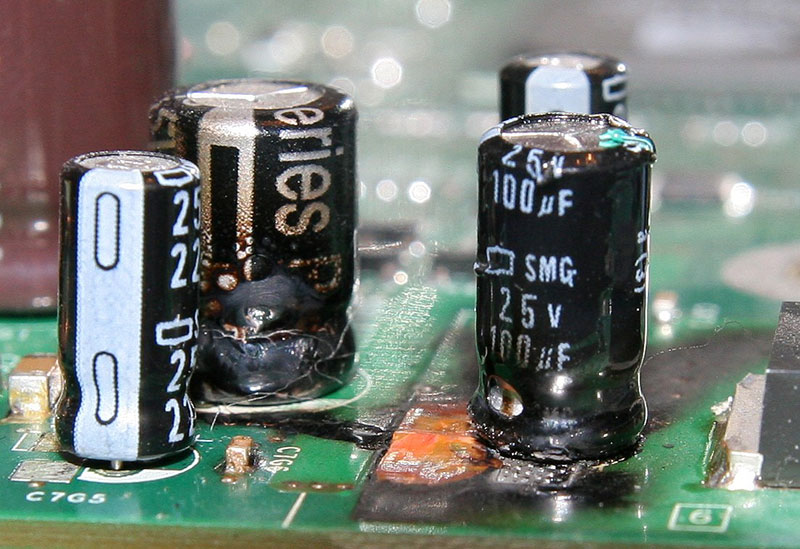
Capacitor polarity is the designation of the positive and negative terminals of a capacitor. This is important because capacitors can only be connected to a circuit in the correct polarity. If a capacitor is connected in the wrong polarity, it can be damaged or even explode.
There are two main types of capacitors: polarized and non-polarized. Polarized capacitors have a positive and negative terminal, and must be connected to a circuit in the correct polarity. Non-polarized capacitors do not have a positive or negative terminal and can be connected to a circuit in any polarity.
For optimal performance, you must orient polarized capacitors in the correct direction since they have positive and negative terminals, making them essential components. Two of the most common polarized capacitor types are electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, both capable of providing incredible power to your circuit design.
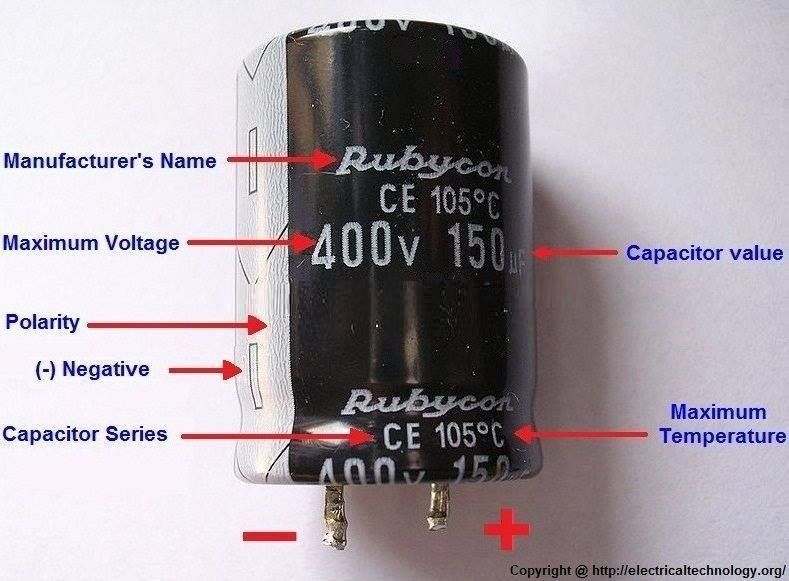
These specialized capacitors leverage a conductive liquid or gel electrolyte to provide far greater electrical storage than traditional capacitor models. Power supplies, audio equipment, and electronic devices everywhere widely use polarized capacitors because of their essential nature with the positive and negative terminals. It's important to note that an electrolytic capacitor has two distinct terminals; the positive is marked "+", whereas the negative carries a "-" sign for easy identification.
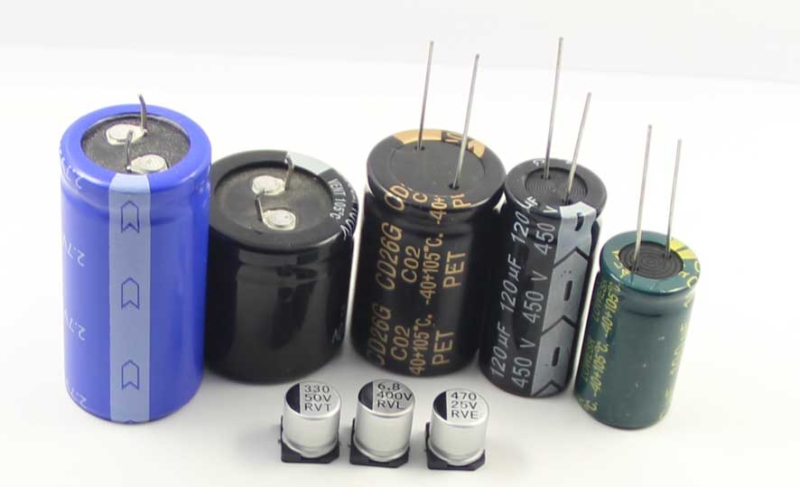

Tantalum Capacitors are unique electrochemical components, that utilize tantalum metal for their anode electrodes. Their remarkable stability and dependability make them a favored choice in electronic devices such as cell phones and computers. These capacitors offer greater tolerance to voltage spikes than electrolytic capacitors, making them exceptionally dependable under extreme circumstances. To easily distinguish between the positive terminal marked with a "+" sign and its negative counterpart indicated by either "–" or stripes - you'll find this feature helpful!
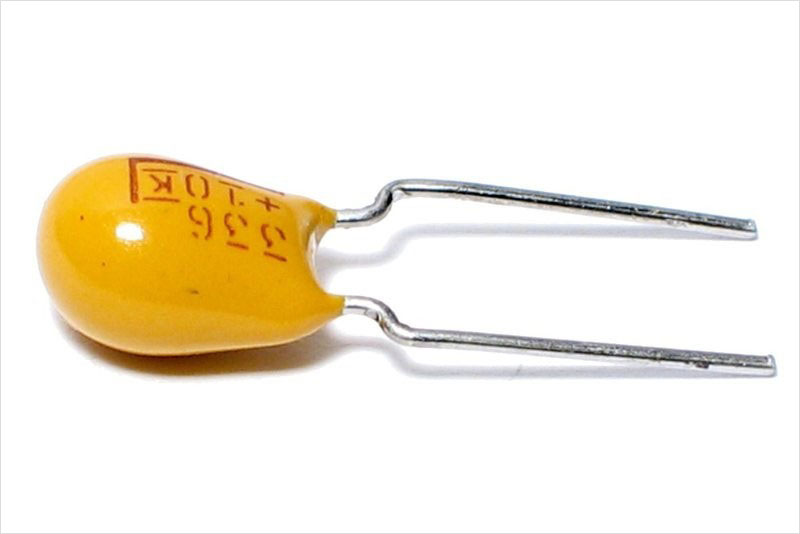

It is critical to correctly attach polarized capacitors as inversely connecting it can result in malfunction, leakage or even explosion. When dealing with polarized capacitors, verifying the polarity markers and ensuring that its positive terminal links to a higher voltage and negative terminal links to a lower voltage are majorly important.
Non-polarized capacitors are a dream come true for any hobbyist, as they have the ability to join in whatever direction you desire without causing any problems. Both ceramic and film capacitors fall into the non-polarized category, making them incredibly versatile components to have on hand.
Ceramic capacitors are a highly reliable and efficient capacitor type with excellent performance. Their small size makes them ideal for use in high-frequency circuits, while their stability at higher temperatures helps to ensure they don't fail when working under intense conditions. What's more, these non-polarized capacitors offer an incredible range of values and feature no polarity markings—ensuring you always get the right level of power decoupling needed!
Film capacitors offer a distinct advantage to any electronics project - stability, efficiency and temperature resistance. With an extensive range of available values and voltage ratings, these non-polarized plastic film dielectrics are ideal for power supplies or audio circuits in devices such as phones or computers. No polarity markings mean that installation is simple too!
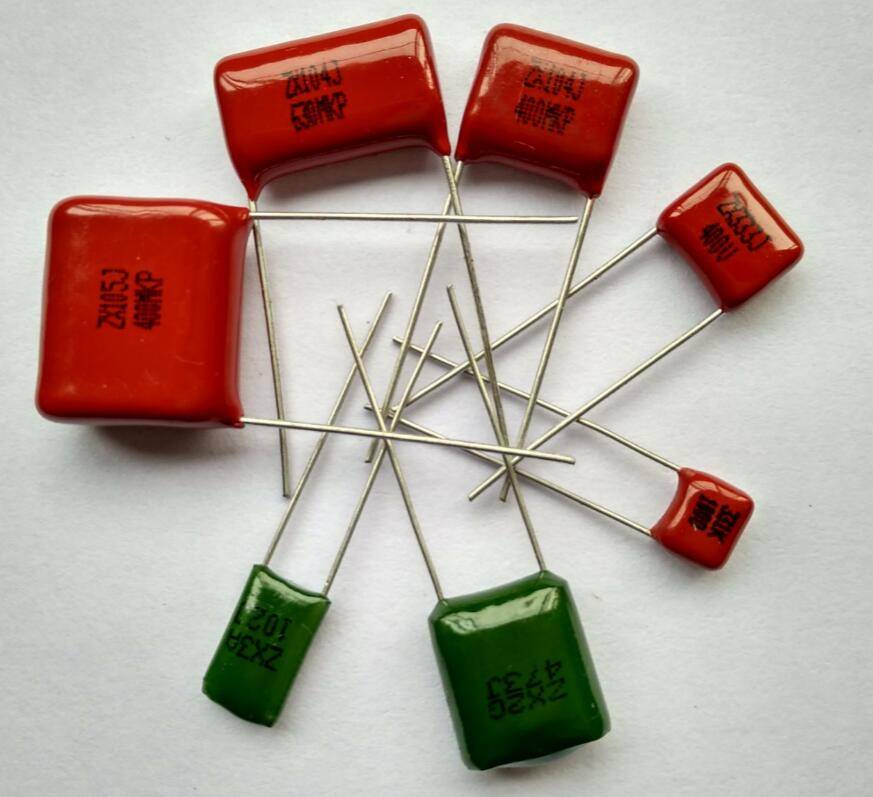

Non-polarized capacitors are an ideal option for circuits that do not require polarity, especially when it is challenging to determine the correct polarity. To ensure your circuit operates optimally, make sure the voltage rating and capacity of your non-polarized capacitor precisely match its needs.
It is of the utmost importance to always observe capacitor polarities – particularly for polarized capacitors, such as electrolytic and tantalum ones. This is because each one has two designated terminals (a positive and a negative), that must be connected in the proper order; otherwise, they can become damaged or even explode! Everyone should understand why it's so important to get this right:
Reversing the polarity of electrolytic or tantalum capacitors can have a range of damaging effects. Here are some repercussions that you may experience if you polarize your capacitor in an incorrect manner:
In summary, reversing the polarity of a capacitor can have several negative effects, including a reduction in capacitance value, an increase in leakage current, an overvoltage condition, and circuit malfunction. To avoid these negative effects, it is important to observe capacitor polarity markings and connect polarized capacitors properly.
Polarized capacitors, such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, typically have polarity markings that indicate their correct orientation. Capacitors often have the following polarity markings:
"+" And "-" signs: The most common polarity marking on capacitors is a plus (+) and a minus (-) sign, which indicate the positive and negative terminals of the capacitor, respectively. The positive terminal is usually longer than the negative terminal.
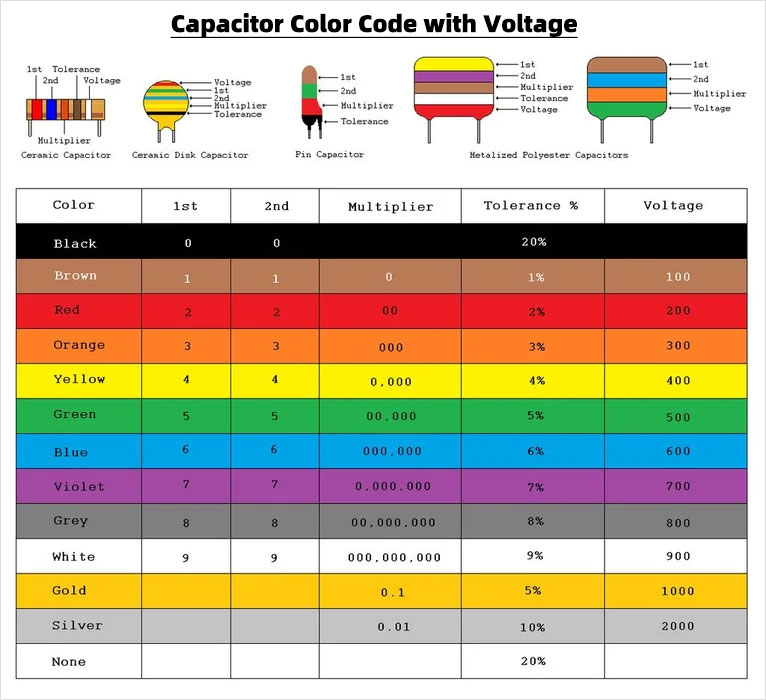
Color coding: Some capacitors have colored bands or stripes that indicate the polarity. The first band or stripe represents the first digit of the capacitance value, and the second band or stripe represents the second digit. The third band or stripe represents the multiplier, and the fourth band or stripe represents tolerance. On polarized capacitors, the fourth band or stripe can represent the polarity.
Arrow: Some polarized capacitors have an arrow marking on the negative terminal to indicate the direction of the current flow.

It is important to note that non-polarized capacitors do not have polarity markings, as they can be connected in any direction without any issues. Verifying the polarity markings on the capacitor and connecting the positive terminal to the higher voltage and the negative terminal to the lower voltage are important steps to take when working with polarized capacitors.
Connecting a polarized capacitor in reverse polarity can cause damage to the capacitor or even lead to a dangerous situation.
To determine the polarity of a capacitor, you can look for polarity markings on the capacitor itself. Here are some ways to determine the polarity of a capacitor:
Polarized and non-polarized capacitors are distinct in nature, which is why they serve different functions. To illustrate their applications, here's a list of where you can find them:
Polarized Capacitors:
Selecting the ideal capacitor for a given application is crucial, as an erroneous choice can cause inadequate circuit performance or even irreparable harm to it.
In conclusion, capacitors are vital electronic components that store electric charge and have multiple applications. Polarized and non-polarized capacitors are the two primary types of capacitors, each with a unique set of characteristics and applicability in different scenarios. Polarized capacitors such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors possess a designated direction of charge and frequently appear in power supply decoupling, audio systems, or timing circuits.
In contrast to these components, non-polarized varieties such as ceramic and film ones do not need an orientation for operating correctly; making them ideal for high-frequency applications like signal filtering or RF circuitry. When selecting the appropriate capacitor for a given application, it is critical to pay attention to polarity markings on polarized capacitors in order to avoid any harm inflicted upon the circuit and ensure proper functioning.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|