
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.com5G is the fifth-generation wireless technology for cellular networks and plays a revolutionary role in telecommunication. It is the most advanced wireless network that is facilitating almost all industries, and its high speed accommodates more devices as compared to its predecessors, which are 4G and 4G LTE.
In this article, we will learn the basics of 5G nationwide and 5G ultra-wideband and will compare them. Both of these technologies are quite similar, but the features like latency, coverage, and speed are significantly different. But before getting into this comparison of 5G nationwide vs. 5G ultra wideband, let’s first have a look at the basics:
Before the practical introduction of 5G services, 4G cellular technology was connecting mobile phones. But in July 2016, 5G technology was introduced, which started working for people in 2019. 5G is defined as:
5G is a new global wireless standard of mobile network services (successor of 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G), used to connect machines, devices and objects virtually and provides high-speed & performance as compared to its predecessors.
It was developed by the 3GGP telecommunications industry, and just like other networks, it is divided into different geographical areas called cells. These cells communicate with high-speed radio waves, and their frequencies are controlled by the base station.
The 5G technology was developed to provide high multi-Gpbs peak speed, low latency, high capacity, and reliable connections to provide the best user experience. The involvement of 5G in different businesses is digitalizing them rapidly and providing the best performance in industries and for common people.
In highly developed areas like the United States, cellular networks are divided into different types based on the frequency band allocated to them. It is because of the great number of users and the requirement for high speed all the time. These standards of allocation are provided by cellular carriers, such as Verizon. 5G nationwide is a low-band 5G network offered by Verizon in the United States. It is designed to have more coverage area and better speed than some other 5G technologies. It has access to the suburban and rural regions, where it provides high speed and has more capacity to accommodate a large number of users.
After 5G nationwide, let’s have a look at what 5G UW means. It is another standard set by Verizon wireless network operators and is not the official name of 5G technology but a marketing name by Verizon. The carriers of 5G UW refer to both mmWave and C bands (you will see them soon in this article) and therefore have greater speed and low latency as compared to other technologies. It is designed to provide the best speed to customers and companies.
The company has focused on providing innovation to customers and industries like robotics, IoT, self-driven cars, etc.; therefore, they have improved the fibres, spectrum, and small geographical coverage areas. This is what the UW means next to 5G.
Just like other cellular technologies, 5G connections also rely on radio wavelengths that can be operated at different frequencies. These are known as the spectrum, and usually, 5G technology is divided into three ranges:
The scope of these bands is given next by keeping 5G vs. 5G UW in mind.
In the radio frequency spectrum, the term low frequency is used for all the bands with a frequency less than 30 MHz. 5G Nationwide uses low-frequency bands in its work because of their penetration capabilities, which make them most suitable for larger areas. These bands support essential mobile services such as voice calls and text messages. Moreover, these are compatible with the existing 4G cellular infrastructure; therefore, they are cost-friendly.
In the 5G UWB, the low-frequency bands are less commonly used as compared to some other bands. The speciality of 5G UWB is video streaming, and related technologies and low-frequency bands are not suitable for these.
C-band is a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum ranging from 4.0 to 8.0 GHz, and it is part of mid-frequency bands. The basic applications of C-band are satellite communication and radar. The high speed of 5G networks as compared to 4G is because of features like the use of C-band.
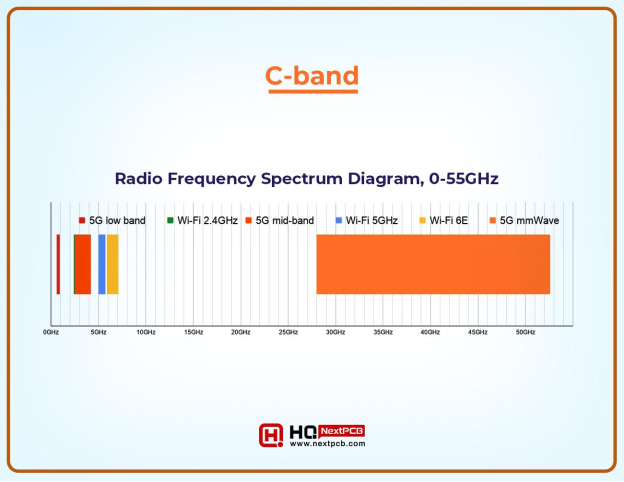
The deployment of the C band in 5G nationwide is responsible for the broader coverage and extensive connectivity. This is the main reason behind the large coverage area. 5G nationwide use these for general mobile data services and as a result, it delivers a consistent and reliable connection. In 5G UWB, it is less commonly used because speed is prioritized over coverage area.
These are known as millimetre waves, and they have a range from 30 to 300 GHz. The short wavelength of these waves has a range of 1-10 mm. These are parts of the extremely high-frequency band (HFB).
In 5G nationwide, there is very little use of mmWaveBands because of the low coverage area. Moreover, these waves are easily blocked by obstacles such as large buildings.
The main use of the mmWaves band is in the 5G UWB because of the highly dense frequency range. The high speed of these bands is a trade-off with the short coverage. These are most suitable where low latency is required for the data-intensive applications.
The 5G ultra-wideband or 5G UWB, has set new standards of speed and connectivity in the communication industry. It is the ideal choice for data-intensive applications, and when people ask what 5G UW is, the answer is the dramatic leap in upload/download speed, even at the rate of multiple gigabytes per second.
When talking about the specifications of a network, three terms are considered the most that are speed, latency, and capacity. The 5G ultra-wideband provides us with the following features:
The 5G UW band provides a peak download speed of 4+ Gbps. Moreover, its upload speed is 200+ Mbps, which is much larger than comparing it with the 30-35 Mbps of 4G and 4G LTE. Think of the case when the 4K ultra HD video clip can be downloaded in a time equal to just a single click.

Entertainment streaming lovers and gamers need 5G ultra-wideband because of the low latency all the time. Moreover, it makes experiences like video chatting and AR so smooth that they provide the best real-time experience. The low latency is also responsible for the zero buffering.
The ultra-wideband has an enormous capacity to handle a great number of people at the time. It means that no matter if the audience in the stadium or airport is using the same network, the 5G ultra band has the capacity to provide the service to all of these without affecting the performance. This is a much larger capacity than the previous versions of networks.
The previous section was about what the 5G UBW provided us, but the answer to what the 5G UBW provided us is still incomplete. Here are some points to understand how these properties of 5G UBW are changing the user experience:
High speed and lower latency result in the best user experiences that were not possible before. The seamless streaming and the crystal clear video chatting and clips are the most important aspects of this network. The online interaction of the user is now much better with this 5G UW speed.

The world is now moving towards automation, and IoT is spreading in every building. The enhanced trend of IoT requires a secure and continuous source to connect the machines together. 5G is revolutionizing the IoT industry, and people are now more interested in using and making the systems connect together.
It allows the IoT to spread at a rapid rate from smartphones to industrial sensors and makes the system more automatic. This is going to change the user’s life at a rapid rate as innovations are now becoming more common.
The 5G UWB is changing all industries at different levels. One such example is the medical industry, where remote surgeries are possible with the help of 5G network. A great deal of practice is required for it, but 5G is making it possible.
Moreover, in industries like transport and manufacturing, products are now more automatic and innovative, and 5G is playing a vital role in them.
The scope of 5G UWB does not end with single industries; it is capable of handling processes in smart cities as well. With the advancement of technologies, people are now working on more automated and better cities, and 5G UWB is boosting their confidence to do so. It helps in real-time data collection among different connected entities. Moreover, to make these projects possible, there is a great deal of communication between the connected infrastructure for processes like traffic management and public services.
Till now, the discussion was about single networks, and the comparison was with the old network types, which are 4G and 4G LTE. Now, we will discuss the comparison of Verizon 5G ultra wideband vs. 5G nationwide.
5G nationwide has a greater coverage area and can reach large rural areas. As a result, it can provide the benefits of 5G speed to a great audience with its strong cellular infrastructure.
The coverage area of 5G UWB is next to 5G nationwide.
The 5G ultra-wideband has greater performance but for a smaller geographical area only. Therefore, it is usually set up in a well-populated smaller area, such as a developed city. The signals are strong, but the coverage area of these signals is low.
The speed of 5G nationwide is much better than the 4G networks, but still. It has no comparison with the 5G UWB. Speed is the main reason for upgrading the network from 4G to 5G, and if the user gets a download speed of multiple gigabytes per second, it is obvious that they will prefer the 5G wideband network.
The 5G nationwide is designed to provide stable signals for a wider area, but when it comes to speed, no one can beat the 5G ultra wideband. The high speed, even for videos and live calling, is an advantage of using the 5G UWB. Hence, when we compare both of these networks, we see that the scope of 5G UW is next to 5G nationwide.
All the devices are not compatible with all frequencies because of the limitations in their structure according to their type. The range of both of these networks is different. In a general sense, we can say that the newer devices are compatible with both of these networks, but usually, the compatibility of the devices is more with the 5G nationwide as compared to the 5G ultra wideband.
The future potential of both of these networks is greater than that of 4G networks. The broad coverage area of 5G nationwide helps it provide connectivity to rural and urban areas on a larger scale. It is spreading at a rapid rate, but the limitations in speed are the reason behind the limited applications.
In the future, it seems the scope of 5G UWB will be greater because of the high speed that is making the world a global village at a greater speed. It has more applications, and technologies like IoT, AR, and VR are now designed according to the workings of 5G UWB to get more benefits from the same components.
Today, we had a great discussion on Verizon Ultra Wideband vs. Nationwide, and we started with the basic introduction of these 5G networks. These are the latest types of high-speed wireless networks that have a specific feature, making them suitable for a particular coverage and speed. We have discussed their working in different frequency bands.
The main difference between these two networks is the coverage area and speed. The 5G nationwide is suitable for larger areas, but it has less speed as compared to the 5G UWB. On the other hand, the 5G UWB has tremendous speed but is limited to smaller urban areas. I hope it was helpful for you to understand the difference.
- New Automated PCB Assembly Quotation System - Order in Just a Few Steps!
- Free PCB Assembly Offer is Now Live
- HQ NextPCB Introduces New PCB Gerber Viewer: HQDFM Online Edition
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|