
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comThe Td value, short for Decomposition Temperature, refers to the temperature at which the PCB material begins to decompose during heating. Simply put, when the PCB is heated to a certain temperature, its material structure starts to change, and this temperature is known as the Td value.
For example, during PCB production, processes like soldering and reflow soldering may expose the board to high temperatures. Understanding the PCB's Td value helps us determine the maximum temperature the material can withstand during these processes, thereby preventing damage caused by excessive heat.
In electronics manufacturing, soldering is a critical step. If the PCB’s Td value is too low, the material may decompose due to high temperatures during soldering, leading to poor circuit connections, component damage, and other issues. Conversely, a higher Td value ensures the PCB remains stable during high-temperature processes, improving the reliability of the manufacturing process.
Case Study: A manufacturer discovered issues like bubbling and delamination on some PCBs after soldering. Upon investigation, it was found that the PCB material had a low Td value, leading to decomposition during soldering. This not only affected product quality but also reduced production efficiency and increased costs.
PCBs are subject to various environmental factors during use, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity. If the PCB's Td value is low, prolonged exposure to temperature variations may cause gradual decomposition, reducing the product's lifespan. A higher Td value enhances the PCB's stability, helping it resist environmental impacts and extend the product's longevity.
For electronic engineers, understanding the Td value of a PCB can guide them in considering the material’s heat resistance during the design phase. This allows for appropriate component layout and soldering techniques, preventing PCB damage due to excessive temperatures. Moreover, during material selection, engineers can choose PCB materials with suitable Td values to meet the specific performance requirements of the product.
Different PCB materials have varying Td values. When selecting PCB materials, prioritize those with higher Td values. For instance, high-performance materials like glass fiber-reinforced epoxy or ceramic substrates typically have higher Td values and can meet the demands of high-temperature environments.
Certain process parameters in PCB production can affect the Td value. For example, controlling the lamination temperature, time, and pressure can enhance the bonding strength of the material, thus improving the Td value. Additionally, advanced surface treatment techniques, such as electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG) or organic solderability preservative (OSP), can improve the PCB's heat resistance.
During PCB manufacturing, heat-resistant additives like flame retardants and antioxidants can be added to enhance the material’s heat resistance, thereby increasing the Td value. However, it's important to consider the impact of these additives on other PCB properties, such as electrical performance and processability.
Proper heat treatment of the PCB can increase its Td value. Heat treatment can relieve internal stresses in the material, increase its crystallinity and stability, and thereby enhance its heat resistance. However, the temperature and duration of the heat treatment must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the PCB.
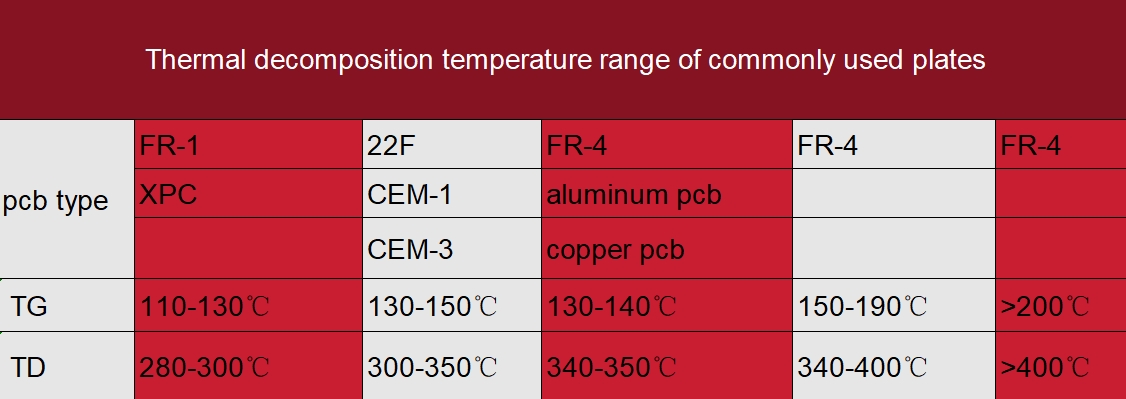
In PCB manufacturing, two critical parameters that engineers and designers often consider are Td (Decomposition Temperature) and Tg (Glass Transition Temperature). Both of these parameters are related to the thermal properties of the PCB material, but they serve different purposes and indicate different aspects of the material's behavior under heat.
Nature of Transition:
Td: Indicates a chemical decomposition of the material.
Tg: Indicates a physical phase change from rigid to flexible.
Temperature Range:
Td: Generally higher, representing extreme conditions.
Tg: Lower, representing the transition to a rubbery state under moderate heat.
Impact on Manufacturing:
Td: Critical during high-temperature processes like reflow soldering. Beyond this temperature, the board may fail.
Tg: Important for ensuring the board's stability during regular operation. Exceeding this temperature may cause mechanical deformation.
While both Td and Tg are important thermal properties of PCB materials, they serve different purposes. Td is primarily concerned with the material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures without decomposing, making it vital for ensuring the board's longevity during manufacturing processes. Tg, on the other hand, deals with the material's transition from a rigid state to a flexible one, which is crucial for maintaining the board's structural integrity during operation. Understanding the distinction between these parameters helps in selecting the appropriate PCB material for specific applications and ensuring the board's performance and reliability.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|