An Introduction to the Widely-Used IPC-2221 Standard
IPC-2221 is a standard for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) that were developed by the Institute of Printed Circuits (IPC), which is now known as the Association Connecting Electronics Industries. The standard provides guidelines for designing reliable and manufacturable PCBs.
IPC-2221 covers a wide range of topics related to PCB design, including materials, the board size, and shape, component placement, trace and space widths, via design, and thermal considerations. It also provides guidelines for documenting and communicating PCB design information.
The standard is intended to ensure that PCB designs are reliable and can be manufactured efficiently and cost-effectively. By following the guidelines in IPC-2221, designers can reduce the risk of errors and improve the quality and consistency of their PCB designs.
Hence, this standard finds widespread application in the electronics sector and is highly regarded as a crucial asset for designers and manufacturers of PCBs.
Materials Considerations in IPC-2221
The IPC-2221 standard offers guidance for choosing materials for PCB designs that meet cost, reliability, and performance requirements. The guide includes important material considerations to take into account.
- Copper thickness of PCB: IPC-2221 gives guidance on the minimum copper thickness needed for PCBs depending on their purpose and the surrounding conditions. The standard also offers advice on choosing a copper weight that meets specific electrical performance requirements.
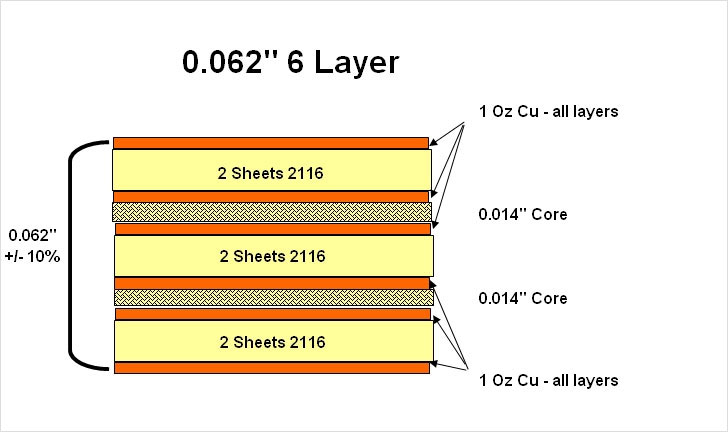
- Substrate materials: The guidelines provided by the standard help in choosing substrate materials based on their electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic are some commonly applicable substrate materials.
- Solder mask materials: The IPC-2221 guideline helps select solder mask materials that fulfill specific performance and reliability criteria such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and adhesion.
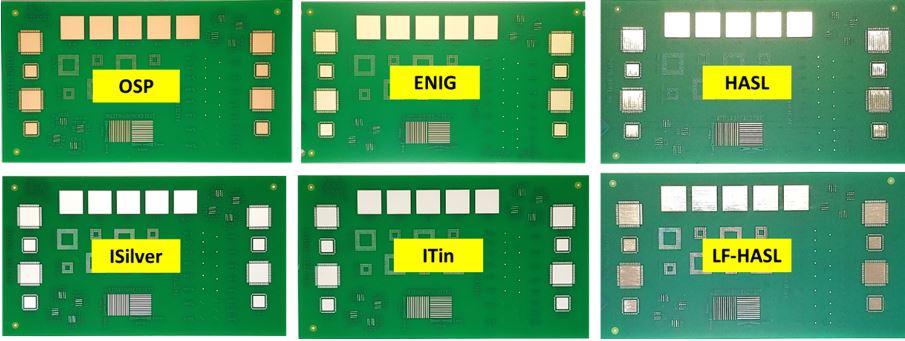
- Surface finish: The standard gives suggestions for choosing surface finishes depending on the PCB's intended usage and design materials. ENIG, HASL, and OSP are some popular surface finish options.
- Conductive trace materials: The guidelines outlined in IPC-2221 help in selecting conductive trace materials based on their electrical performance and cost. While copper is widely applicable as a trace material, gold and silver are possible to use in some specific applications.
- Dielectric materials: The standard guidelines help choose dielectric materials based on their electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. Moreover, for high-speed and RF applications, it's crucial to consider the material's dielectric constant.
- Environmental considerations: The standard offers guidance on picking appropriate materials suitable for specific operating conditions such as environments with high temperature, humidity, or corrosion.
Therefore, designers can ensure that PCB designs meet performance, reliability, cost requirements, manufacturability, and environmental safety by adhering to the materials selection guidelines in IPC-2221.
Board Size and Shape Guidelines in IPC-2221
The IPC-2221 standard offers guidance on designing PCBs with various sizes and shapes. The standard covers important considerations related to board size and shape.
- The aspect ratio of PCB: IPC-2221 guidelines provide recommendations for choosing aspect ratios based on the board size and intended use, where the aspect ratio is defined as the ratio of the board thickness to the smallest feature size, such as the trace width or hole diameter.
- Board edge design of PCB: The guidelines in the standard help design board edges to reduce the likelihood of harm during handling and assembly. These guidelines involve stating the minimum edge clearance required and adding chamfers or bevels to prevent sharp corners.
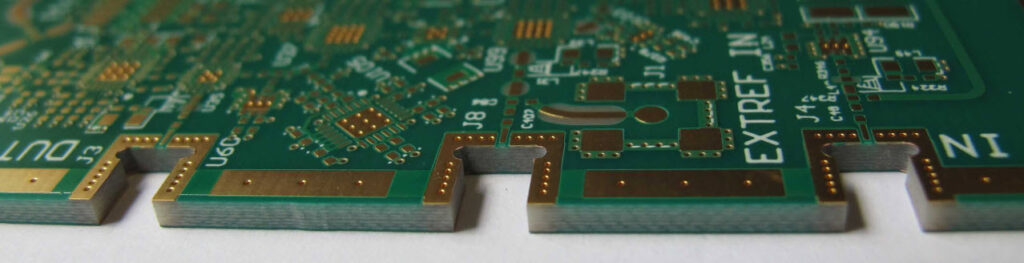
- Board size limitations of PCB: The IPC-2221 offers guidance on how to design printed circuit boards (PCBs) of varying sizes. Because of that, this takes into account the limits of the manufacturing process and the intended purpose of the board. The guidance involves setting minimum and maximum dimensions for the board, as well as accounting for panelization and manufacturing tolerances.
- Placement of mounting holes on PCB: The guidelines in the standard dictate where to place mounting holes on a board, taking into account the minimum distance from the board edge and spacing between holes. These guidelines aim to ensure that the board remains structurally sound and secure when mounted.
- PCB thickness: The IPC-2221 offers guidance on how to select the correct thickness for a board, taking into consideration its intended use and environmental factors. The guidelines outline the smallest and largest thickness allowed, while also considering how the thickness may affect manufacturing processes such as drilling and plating.
Component Placement Guidelines in IPC-2221
The IPC-2221 standard offers guidelines for placing circuit-board components in a way that guarantees electrical performance, manufacturability, and reliability. Therefore, the component placement factors addressed in the standard are:
- Orientation of PCB: The standard gives instructions on how components should be positioned based on their purpose and the design's electrical and mechanical requirements. Because orienting components appropriately helps to minimize electrical path length and prevent interference between nearby components.
- Clearance and spacing of PCB: The guidelines in the standard determine the appropriate distance between components based on their size and intended use. Moreover, these guidelines aim to prevent electrical shorts and ensure proper mounting and PCB soldering of the components.
- Trace routing: The standard gives instructions on how to route traces between components, taking into account their intended use and electrical needs. When routing, it's important to keep the length of electrical paths as short as possible and to prevent any interference between adjacent components.
- Thermal considerations of PCB: Moreover, this standard offers recommendations on where to place components to achieve the best thermal performance. Therefore this involves keeping heat-generating components away from sensitive ones and ensuring that components have enough thermal relief to avoid thermal stress.
- Accessibility: The guidelines in the standard ensure that components are easily accessible and can be replaced without difficulty. Therefore this involves avoiding the placement of components under other components or near the edges of the board where they may be difficult to access.
PCB designers can ensure that their designs are dependable and can fulfill the intended use by adhering to the guidelines provided in IPC-2221 for component placement. Additionally, Proper attention to component orientation, trace routing, thermal considerations, and clearance and spacing can aid in enhancing the reliability and performance of the PCB.
Trace and Space Guidelines
IPC-2221 offers instructions for the least trace and space specifications on PCBs to guarantee electrical performance, reliability, and manufacturability. Therefore, we discuss some vital trace and space aspects outlined in the standard below.
- Trace width of PCB: The guidelines in the standard assist in selecting the appropriate trace width for a PCB based on two factors: the amount of current the trace can carry and the PCB manufacturing process.
For carrying more current, wider traces are necessary.
- Space width: The standard provides guidelines for selecting appropriate space widths based on the manufacturing process used to produce the PCB. In order to prevent electrical shorts and ensure proper soldering of traces, the space widths should be wide enough.
- Impedance control: The standard includes instructions on how to control impedance on the PCB, which involves determining the appropriate trace width and spacing. Maintaining impedance is essential for high-speed and RF applications since it helps preserve signal integrity.
- Differential pair routing: The standard offers directions on how to route differential pairs on a PCB effectively. Maintaining a uniform impedance and minimizing interference between neighboring traces are the reasons for doing this.
- Via spacing of PCB: The standard offers recommendations for the selection of suitable spacing depending on the method used to manufacture the PCB. Therefore, it is essential that the via spacing is sufficient to prevent any electrical shorts and to allow for proper plating of the via.
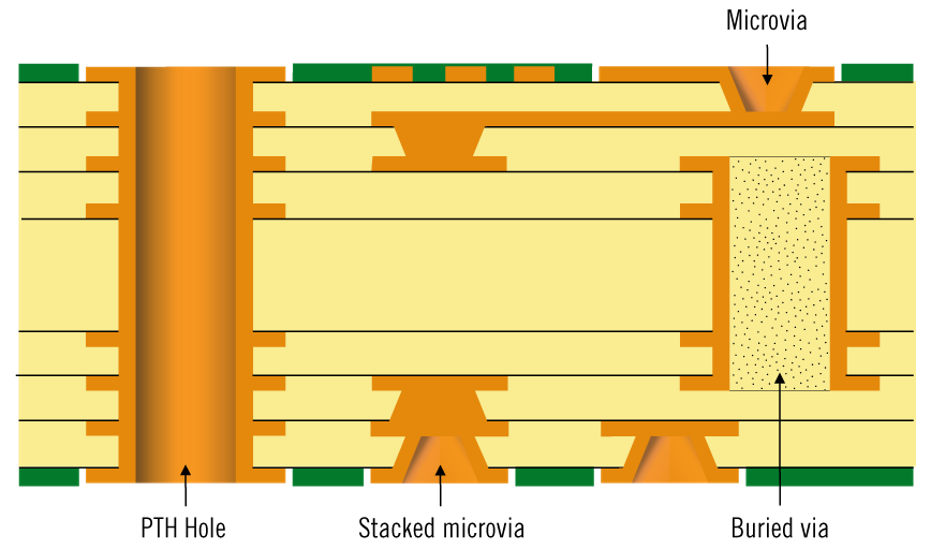
PCB designers can ensure their designs meet the necessary electrical performance and reliability standards, as well as manufacturing and environmental safety requirements, by adhering to the trace and space guidelines outlined in IPC-2221. Proper trace width and spacing selections, impedance control, and differential pair routing are all factors that can improve the PCB's electrical performance and reliability.
Via Design Guidelines
The IPC-2221 standard offers advice on designing vias for printed circuit boards (PCBs) to guarantee electrical performance, reliability, and ease of manufacturing. The standard covers essential factors to consider when designing vias.
- Via size of PCB: The standard offers guidance on choosing suitable via sizes depending on the intended purpose and the PCB manufacturing process employed. Vias must be of sufficient width to handle the necessary current and guarantee appropriate plating.
- Via spacing of PCB: The guidelines in the standard help in selecting the right spacing for printed circuit boards (PCBs) based on their intended use and manufacturing process. The space between vias should be sufficient to avoid electrical shorts and proper plating of the vias.
- Via placement of PCB: The guidelines in the standard specify where to place vias on the PCB according to the design's intended use and its electrical and mechanical requirements. To ensure a minimal length of electrical paths and prevent interference between adjacent components, vias should be positioned carefully.
- Via types: The guidelines outlined in the standard help choose the appropriate type depending on the design's intended purpose and its electrical and mechanical requirements. To make the board smaller, you can use blind and buried vias. Through-hole vias are more prevalent and offer better electrical performance.
- Via plating: The standard gives instructions on how to plate vias to create dependable electrical connections between different layers of the PCB. The plating thickness and the type of plating chosen must be based on the intended purpose and the PCB manufacturing process.
Thermal Considerations in IPC-2221
The standard IPC-2221 offers guidance on thermal considerations for the design of printed circuit boards (PCBs), which includes managing heat dissipation and preventing thermal damage. Some important thermal factors addressed in this standard are summarized as follows:
- Thermal conductivity of materials: The guidelines in the standard help in selecting materials that have suitable thermal conductivity for the intended use. Choosing materials that have higher thermal conductivity can enhance the dissipation of heat effectively.
- Thermal relief: The standard offers instructions on how to create thermal relief patterns around copper pads. This helps make soldering easier and prevents too much heat from building up during the process.
- Copper weight of PCB: The standard offers guidance on how to choose the right amount of copper for efficient heat dispersion. You should base your selection on both the current carrying capacity of the trace and the anticipated temperature increase resulting from Joule heating.
- Thermal vias: The standard offers instructions for creating thermal vias that can dissipate heat from components on the PCB that generate heat. By reducing the temperature increase of the PCB, thermal vias can prevent thermal damage.
- Thermal management of PCB: The standard gives instructions on how to create thermal management systems that can manage the dissipation of heat in the PCB, including the use of heat sinks and fans. These systems can aid in avoiding thermal damage and enhance the PCB's dependability.
IPC-2221 Implementation and Benefits
If you follow the guidelines in IPC-2221, which is a widely recognized and accepted standard in the printed circuit board (PCB) design industry, you can enjoy many benefits as a designer, manufacturer, or end-user of PCBs.
- Improved manufacturability: IPC-2221 offers guidance on how to design PCBs in a way that makes them easy to manufacture, lowers the chances of errors, and reduces the need for rework.
- Increased reliability: PCB designers can make sure their designs meet the required electrical and thermal performance and reliability by adhering to IPC-2221 guidelines. This can prevent failures and increase the lifespan of the PCB.
- Cost savings: IPC-2221 guidelines can help reduce the cost of manufacturing PCBs by reducing the need for rework, improving yield, and reducing the risk of errors.
- Consistency of PCB: IPC-2221 is a set of standardized guidelines for designing PCBs. This helps to maintain consistent standards across various suppliers and vendors, resulting in better PCB design and manufacturing.
- Environmental benefits: Designers can reduce the use of hazardous materials and improve the environmental impact of their PCB designs by following the IPC-2221 guidelines.
By adhering to IPC-2221 guidelines, you can ensure that your PCB designs meet necessary performance and reliability standards. Additionally, following these guidelines can improve your design's manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Finally, IPC-2221 is a standard that offers extensive suggestions for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs). Its goal is to ensure reliability, and manufacturability, and meet the required performance standards. The standard covers various design aspects, such as board size and shape, component placement, trace, and space, via design, thermal considerations, and more.
Designers of PCBs can ensure that their designs meet the intended performance and reliability requirements, while also being possible to manufacture and cost-effective, by following these guidelines.
Following IPC-2221 guidelines can offer many advantages such as enhanced production, reliability, consistency, cost-effectiveness, and environment-friendly operations. IPC-2221 is an indispensable resource for both PCB designers and manufacturers, enabling them to create designs that meet performance specifications, are easily manufactured, and are affordable without harming the environment.





