
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comPrinted Circuit boards can cost from 50 cents to $500 to produce. There are several factors a manufacturer considers in determining PCB costs. If you are in the market to design a Printed Circuit Board, this guide provides factors to consider that could increase or decrease Printed Circuit Board Costs.

Materials used in manufacturing PCBs determine the price of PCBs. Depending on the PCBs, they have varied composite materials, potentially increasing or reducing PCB costs. Three types of Printed Circuit Boards available in the market are rigid, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs.
In addition, board size can determine the number of materials required to design a PCB. Working with fewer materials can cut material costs. Other factors to consider when selecting materials include Temperature reliability, thermal performance, mechanical properties, and signal performance. All these factors are integral to PCB performance and reliability in extreme conditions.
There is a general idea that with more layers on the PCB, there will be a resulting increase in PCB cost. Increasing the number of layers would mean more steps in production, more materials used, and more time in designing and manufacturing, such as Printed Circuit Boards.
However, adding two PCB layers does not necessarily mean that the PCB cost will be double. Instead, there will be a marginal increase in the price (usually 30% to 40%). Also, additional layers on already layered PCBs may not necessarily result in a marginal price increase. The cost factor regarding layer amount varies from design complexities and manufacturer to manufacturer.
In reverse situations, Reducing the layers does not mean there will be a reduction in PCB costs, as it may involve complex technology and design practices. Yet, the complexity and design of PCBs are kept constant. A change in PCB cost depends linearly on the number of layers. Use a free online DFM PCB Gerber viewer to review your PCB layer by layer and assist you to reduce cost.
The size of a PCB panel determines its cost. More size means more space to add components and circuits for its intended application. Larger PCBs are usually expensive since they are applicable in medium to large devices, for example, a Laptop’s PCB or an industrial machine PCB.
Smaller PCBs are often cheaper and require fewer components to carry out their intended use case. Smaller PCBs are found in digital wristwatches. PCB dimensions differ from the manufacturer, but here are three common dimensions used in manufacturing Printed Circuit boards:
It is essential to note that while PCB sizes will differ in price, the space occupied by each component also affects PCB cost. Although manufacturers recognize the dimensions of PCBs, they base their PCB costs on these dimensions. As such, a small but high volume (due to more components on the board) PCB will be cheaper than a large but low-volume PCB.
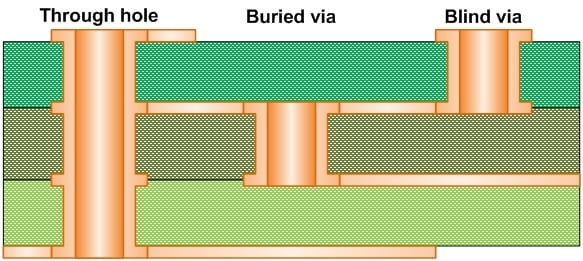
Based on design and specification needs, an electronic board may require vias that traverse all the layers of the PCB. Vias means electrical connections between different layers of a Printed Circuit Board. Via can be a relatively small hole made through the PCB that crosses two or more adjacent layers.
Some types of vias are based on the number of layers they pass through. They are through hole via (which passes through all the layers of the PCB), buried via (which is inside the PCB and therefore does not affect external layers), and bind via (which starts at one outer end and may cross one layer or two without joining the opposite side of the PCB).
Vias do not directly affect PCB costs as they depend on the number of layers on the Printed Circuit Board and the via used (as explained above).
Relays in circuit boards is an electrical switch that enables proper PCB functioning and devices. PCB relay circuits range from electromagnetic relays to hybrid, thermal and solid-state relays.
Electromagnetic relays contain an electromagnet that receives electric signals and converts them into mechanical action of closing and opening the circuit. An electromagnetic PCB relay working operation involves electromagnetic field induction in designing a PCB board.
When electric power gets to the relay coil, it causes the armature to move, enabling the opening or closing of the contacts. Finally, the working operation of Relays in a PCB circuit can affect the PCB costs. If the PCB requires more than one relay, it will be designed to accommodate more power, making it more expensive.
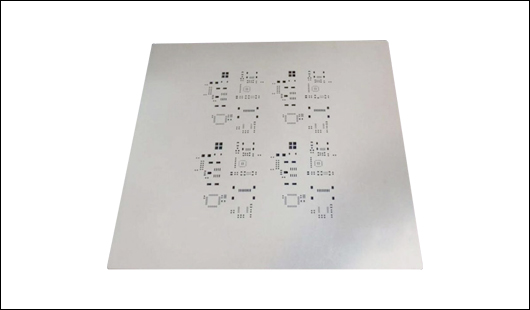
A generic PCB stencil comprises a stencil frame, wire mesh, and steel sheets. PCB stencils are often called steel mesh. Its main function is to deposit solder paste in the right amounts on the Printed Circuit Boards.
Many holes in the stencil correspond to positions that must be printed on the PCB. When in use, the PCB is placed under the stencil, then solder paste is gently poured into the PCB through the specific hole on the stencil. If the holes do not block paste deposition, more will be deposited on the PCB.
There are different kinds of PCB stencils, including Laser stencils, electropolishing stencils, step stencils, bonding stencils, nickel plating stencils, electroforming stencils, and etching stencils. They have different modes of operation, and your choice of PCB stencil can increase or decrease your PCB costs.
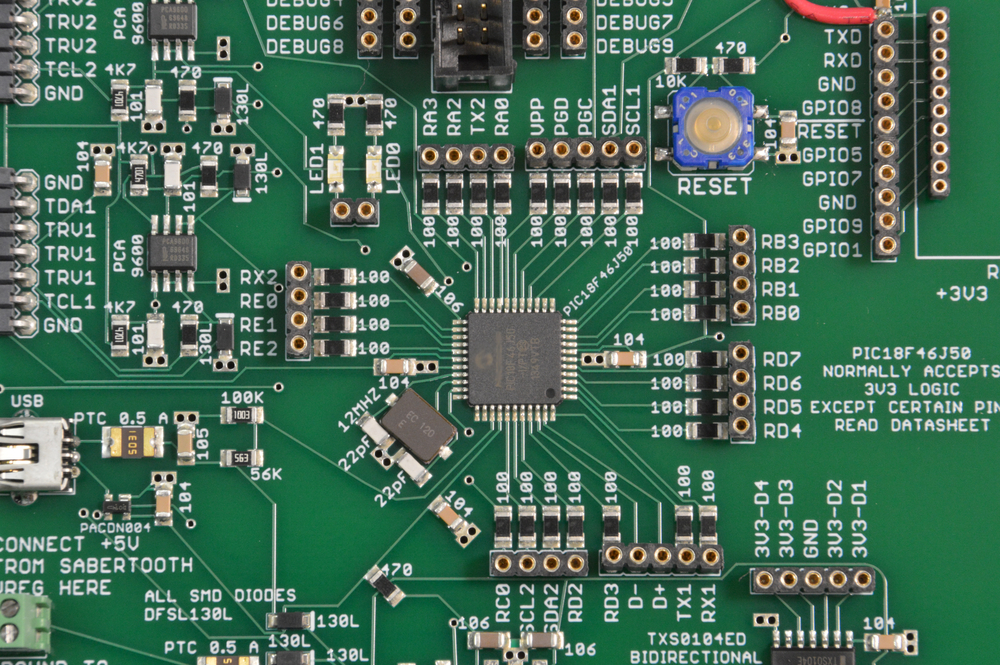
Silkscreens are additional processes in PCB manufacturing. They are layers of ink traces used to identify circuit components, test points, warning symbols, marks, and others. A detailed PCB silkscreen can help manufacturers and consumers identify specific PCB components.
However, the use of silkscreen on PCBs is optional. If you did not opt for silkscreen in the PCB design process, the PCB costs would reduce. Based on the customer's needs for adding silkscreen, various brands could potentially hike the PCB costs. Yet, many manufacturers provide silkscreen free of charge.
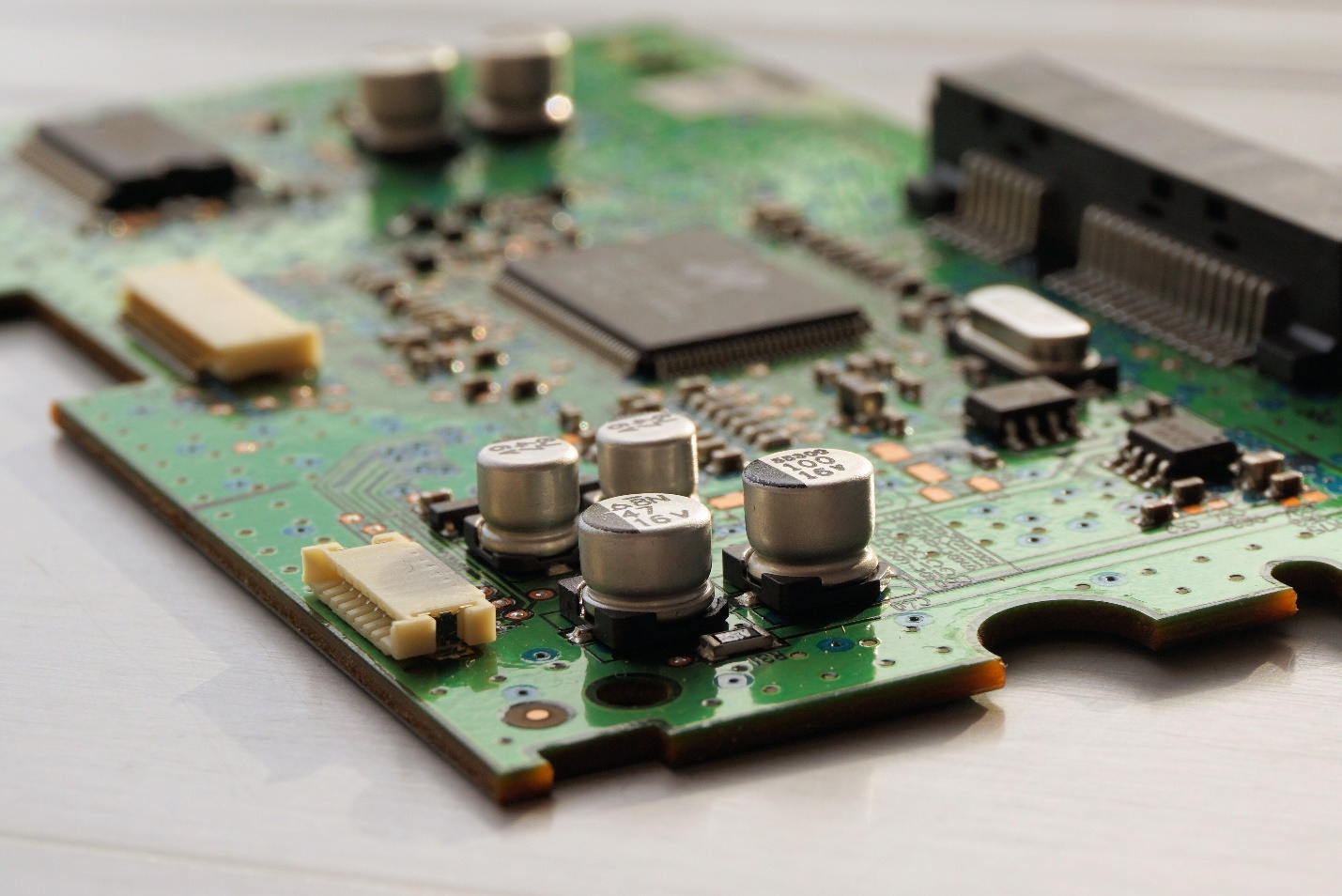
The number of electronic components on a circuit board can either increase or reduce PCB costs. It will benefit when designing a PCB; fewer components are applied to the circuit board. Fewer components mean lesser cost in producing such PCBs and vice versa.
It is imperative to understand the supply-demand chain of specific electric components when determining the cost of PCBs. Scarce raw materials or scarce components in the market can make such parts expensive and add to the PCB cost.
PCB Test is an essential process that PCB manufacturers must carry out to prevent shipping unreliable or insufficient PCBs. There are several tests that manufacturers carry out to ensure they ship PCBs to consumers. However, the most advanced test is in -circuit testing (ICT).
ICT aims at covering almost all the components on the printed circuit boards, including Resistors, Inductors, capacitors, transistors, fuses, switches, and diodes. An extensive test such as ICT is expensive, but if you manufacture bulk PCBs, the price of such tests is worthwhile. ICT test takes less than a minute, which is faster than traditional tests.
The cost of manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards is essential when considering the kind of labor to employ. Selecting highly skilled labor will increase your labor costs and PCB costs.
Depending on your layer count or material needed in your PCB design will affect the labor costs, skilled or unskilled. If you want your PCB design and assembly labor to be cost-effective, you can use low-skilled labor and overhead costs.
Turnaround time involves the time required for a manufacturing process to complete and satisfy the buyer’s request.
There is an inverse relationship between Expected Turnaround time and PCB costs. If PCB boards are needed within a shorter time frame, the costs will increase as more labor and designers are involved to ensure the PCB is designed, manufactured, and shipped to the customers at a reduced timeframe.
However, if the Expected Turn around time is not fixed or standard, the cost of PCBs will remain unchanged or becomes cheaper. Do note that ordering and shipping times affect the price of your PCB. You have to pay more if you want your PCB delivered as soon as possible.
Simple economics shows that the more products ordered (especially bulk orders), the lower the cost per unit. In PCBs’ standard design and manufacturing, and assembly, manufacturers have a fixed price per square inch for each quantity ordered.
However, when a customer needs bulk orders of PCB, the manufacturer can offer a variable cost per square inch. Other factors like design complexities, the material used, and components could affect the price of PCB regardless of the quantity.
The packaging of Printed Circuit Boards can be a sure way to increase the product’s longevity. Also, the kind of packaging used in PCBs can offer some protection. It is essential to design and use your packaging for specific purposes only.
Packaging materials should be cheap, durable, and long-lasting for your project. If you use expensive packaging material, you could exceed your budget and consequently increase your PCB costs.

Flexible PCBs' raw materials are polyester film or polyester amide; Their characteristics include thin, high assembly density, higher flexibility, and bendable and foldable, which are uncommon in rigid Printed Circuit Boards.
They can withstand multiple twists, bends, and folds while retaining their operations, offering good heat dissipation functionality. Many factors influence flexible PCB costs.
Other Factors include panel utilization, size and volume of flexible PCBs, differences in geographic regions, and surface finishes that influence the price of flexible PCBs.
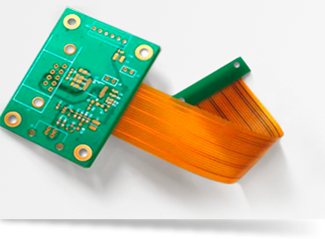
Rigid-flex PCBs are hybrid boards consisting of internal flex and external rigid layers. Rigid-flex PCBs are approximately seven times more expensive than traditional rigid PCBs. The price range This price results from the kind of raw materials required.
Even though Rigid-Flex PCBs use materials common to rigid and flexible PCBs, such as core laminate, copper foil, laminates (flexible), prepreg, bond plies, and cover layers, there are distinct differences in the design process.
The no-flow prepregs are a vital component to designing a Rigid-Flex PCB successfully. No flow prepregs generally cost more than traditional FR4 and polyimide prepregs (up to ten times more expensive).
No-flow prepregs come in two variants (106 and 1080) and are thin glass fabrics. This limitation makes it difficult for Rigid-flex PCB manufacturers to use lower costs and thicker fabrics than traditional rigid PCB utilities.
In addition, Rigid-flex PCBs separate individual components before the final assembling of the parts into the last board. This process further increases the design process and circuit complexity, thereby increasing cost.
The manufacturing yield of Rigid-flex PCBs adds to the overall costs. Combining dissimilar materials with different stability characteristics requires expertise, specialized machines, and software tools. As a result, the yield in rigid-flex manufacturing is reduced than in traditional rigid or flexible circuits.
As a manufacturer, reducing PCB costs on Printed Circuit boards while retaining optimum performance is essential. As consumers, it is necessary to consider factors that can minimize final PCB costs to avoid breaking the bank.
The average price of a Printed Circuit Board ranges from $0.02 to $0.05 per square inch. There are dozens of factors that could affect the cost of a Printed Circuit Board. All these factors have a linear relationship with PCB costs.
The cost per square Inch of a PCB varies directly with the board size, volume, number of layers, and board complexity. Also, the number of electric components must be reduced on the circuit board to minimize PCB costs.
The cost of Wholesale PCBs ranges from $1 to $500. While these costs vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, wholesale PCB costs are relatively cheaper. However, purchasing Printed Circuit Boards at wholesale price is beneficial if you plan to buy a significant number of PCBs.
Printed Circuit Boards are the core of electronics. Despite their complexities and design, knowing how much they cost is imperative. This guide has provided factors to consider when you want to purchase or manufacture a Printed Circuit Board.
It is essential to consider these factors as you can streamline your PCB designs according to your budget. Also, the various types of PCBs and costs were thoroughly explained in this guide for consumers who wish to know the kinds of PCBs available in the market.
Are you looking for a specific kind of PCB? Or are there factors you wish to determine if they influence PCB costs? Kindly contact us via email or support, and we will gladly give you an expert-led answer.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|