
Support Team
Feedback:
support@nextpcb.comHDI (High-Density Interconnect Board) is a compact board designed for small-volume users. Compared to ordinary PCB, the most significant feature of HDI is the high density of wiring, the difference between the two is mainly reflected in the following 4 aspects:
HDI board is the traditional double-sided board as the core board, through the continuous accumulation of layers laminated from. This way by the continuous accumulation of layers of the board is also known as the accumulation of multilayer boards (Build-up Multilayer, BUM). Compared to conventional boards, HDI boards have the advantages of being "light, thin, short, and small".
HDI's electrical interconnection between the layers of the board is achieved through the conductive through-hole, buried via, and blind via the connection. Different from the ordinary multilayer PCB, HDI boards are designed with a large number of micro-buried blind vias.
Ordinary PCB usually is drilled by mechanical method, while HDI PCB drilled by laser. So the number of layers and aspect ratio of HDI PCB is often increased.
HDI board's high density is mainly reflected in the hole, line, pad density, and interlayer thickness.
Micro-Through Via. HDI circuit board contains blind holes and other micro-conductor hole designs. There are main performances in the two aspects. At first, micro-hole and hole-forming technology in diameter of less than 150μm. Second, cost, production efficiency, hole precision control, and other aspects of the high demand. In traditional multilayer circuit boards, there are only through holes without tiny buried blind holes.
Refinement of line width and line spacing. Its main performance in the wire defects and wire surface roughness requirements are increasingly strict. General line width and line spacing of no more than 76.2μm.
The high density of pads. The density of welded joints is greater than 50 per square centimeter.
The thinning of the dielectric material thickness. It is mainly manifested in the trend of the thickness of the interlayer medium to 80μm or below, and the requirement of thickness uniformity is more and more strict, especially for the high-density plate and packaging substrate with characteristic impedance control.
HDI PCB can not only make the end product design more miniaturized but also meet higher standards of electronic performance and efficiency at the same time.
The increased interconnect density of HID PCB allows for enhanced signal strength and improved PCB reliability. In addition, HDI boards have better improvements for RFI, EMI, static discharge, thermal conduction, etc. HDI also uses all-digital signal process control (DSP) technology and a number of patented technologies, with a full range of adaptable load capacity and strong short-time overload capability.
As can be seen from the above, both the volume and electrical performance of the circuit board, HDI are better than ordinary PCB. Where there are two sides to the coin, as high-end PCB manufacturing, HDI PCB manufacturing threshold, and process difficulties are much higher than ordinaryStack-up of HDI PCB:
PCBs. So more problems need to pay attention - especially buried holes plug holes.
The core pain point and difficulty of HDI manufacturing is the buried plugging hole. If the HDI buried hole plugging is not done, there will be major quality problems, including uneven board edges, uneven thickness of the dielectric, pads with pits, and other states.
|
Feature |
HDI PCB |
Traditional PCB |
|
Layer Count |
Typically 6-12 or more |
Usually 2-4 layers |
|
Via Types |
Through-hole, Blind vias, Buried vias |
Primarily Through-hole vias |
|
Line Width & Via Size |
Finer lines and smaller vias |
Larger lines and vias |
|
Functionality |
Miniaturization, High performance, Design flexibility |
Standard functionality |
|
Manufacturing Complexity |
More complex and precise |
Less complex |
|
Cost |
Potentially higher initial cost |
Lower initial cost |
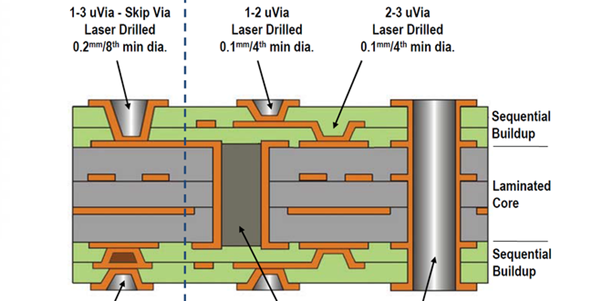
The stack-up of an HDI PCB is a critical blueprint that defines the arrangement and composition of its various layers. Here's a breakdown of the key components and how they differ from traditional PCBs:
Surface Layers: Similar to traditional PCBs, HDI PCBs have top and bottom surface layers that provide connection points for electronic components through solder pads. However, due to the higher density of components often used in HDI PCBs, the surface design needs to be meticulously planned to ensure proper routing and component placement
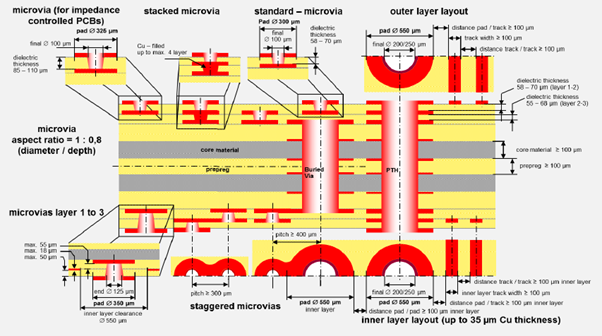
The fabrication of HDI PCBs is a complex and precise process, requiring advanced technology and expertise. Here's how it differs from traditional PCBs:
HDI PCBs are used in consumer electronics, telecommunications, automotive, medical devices, aerospace, industrial equipment, and IoT devices. They enable compact, high-performance electronic systems with improved reliability. HDI technology supports miniaturization, high wiring densities, and signal integrity, making it essential for modern electronics.
Not all board factories have the ability to do well in HDI, but NextPCB has been working on this for over 15 years. Today, NextPCB HDI has its own complete system, the entire process is not outsourced, spending a lot of money to purchase advanced equipment, and all quality acceptance standards have been used IPC2 standards, such as hole copper thickness ≧ 20μm, to ensure high reliability.
Still, need help? Contact Us: support@nextpcb.com
Need a PCB or PCBA quote? Quote now
|
Dimensions: (mm) |
|
|
Quantity: (pcs) |
|
|
Layers: 2 |
Thickness: 1.6 mm |
|
|
|